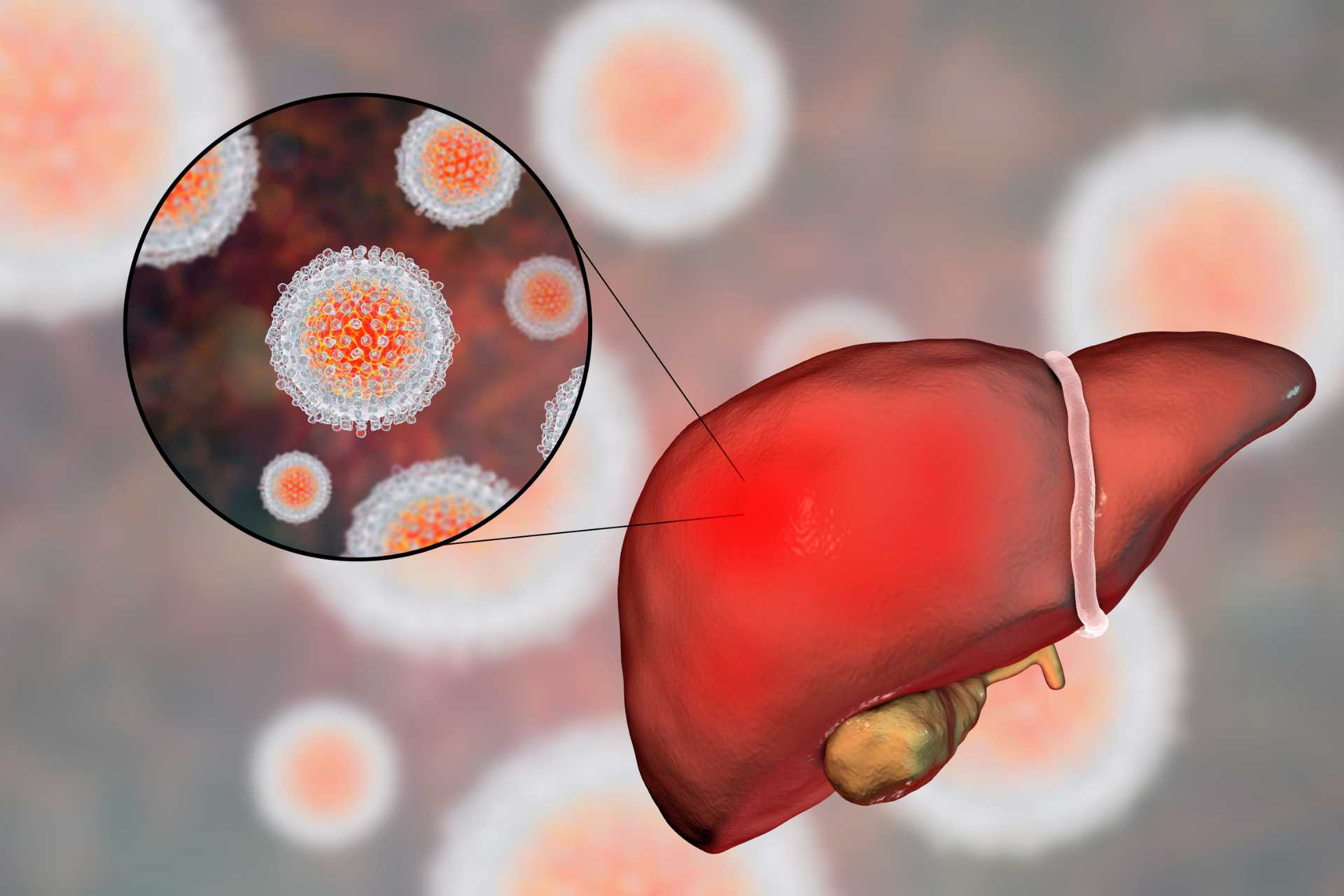
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) primarily targets the liver, leading to a wide range of symptoms that may appear both in the acute and chronic phases of infection. While some individuals may experience mild or no symptoms during the early stages, others may encounter flu-like signs that gradually progress. The infection can remain undetected for years due to its subtle onset, which makes awareness and timely medical consultation crucial.
Common symptoms of HCV include general signs of infection such as fatigue, fever, nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhea, joint pain, and muscle pain. These symptoms are linked not just to the virus itself but to the body's immune response trying to fight off the infection. As the immune system works against the virus, it causes inflammation and related discomfort that can affect a person’s daily life significantly.
More specific signs related to liver dysfunction become noticeable as the infection progresses, especially in chronic cases. Jaundice, which presents as a yellowing of the skin and eyes, is a clear indication of liver involvement. Dark-colored urine and pale or chalky stools also occur due to the build-up of bilirubin—a substance processed by a healthy liver. These signs signal that the liver’s ability to function properly is compromised.
One of the more concerning symptoms includes unusual bleeding and bruising. The liver produces proteins that help blood to clot, so when it's not functioning properly due to HCV, there is a higher risk of prolonged bleeding or easy bruising. These symptoms highlight the severity of liver involvement and are often more persistent in chronic hepatitis C infections compared to the acute stage.
While acute hepatitis symptoms may resolve naturally over several weeks or months, chronic hepatitis C symptoms often linger and can lead to serious complications such as liver failure. Individuals experiencing these signs should consult with an internist doctor immediately. Whether the cause is HCV or another liver-related illness, prompt medical evaluation is essential to prevent further health deterioration and begin appropriate treatment.